NGINX pronounced in English as "engine-ex", is a famous open source web server software. In its initial version, it worked on HTTP web servers. However, today it also serves as a reverse proxy, HTTP load balancer, and email proxy for IMAP, POP3, and SMTP.
This software was officially released in October 2004. The software's creator, Igor Sysoev, started his project in 2002 as an attempt to solve the C10k problem. C10k is the challenge of managing ten thousand connections at the same time. Today, web servers have to handle an even larger number of connections. For that reason, NGINX offers an asynchronous, event-driven architecture, a feature that makes NGINX one of the most reliable servers for speed and scalability.
Due to its excellent ability to handle many connections and its speed, many high-traffic websites use the NGINX service. Some of these internet giants are Google, Netflix, Adobe, Cloudflare, WordPress.com and many more.
How does NGINX work?
Before we delve deeper into what NGINX is, let's review how a web server works. When someone makes a request to open a web page, the browser communicates with that website's server. The server then finds the requested files for the page and sends them to the browser. This is just the simplest type of request.
The above example is also considered a simple thread. Traditional web servers create a single thread for each request, but NGINX doesn't work that way. As we mentioned before, NGINX works with an asynchronous and event-driven architecture. This means that similar threads are managed under a worker process, and each worker process contains smaller units called worker connections. This entire unit is responsible for handling request threads. Worker connections deliver requests to a worker process, which will also in turn forward it to the master process. Finally, the master process provides the result of those requests.
It may seem simple, but a working connection can serve up to 1024 similar requests. Because of that, NGINX can process thousands of requests without any difficulty. This is also why NGINX became a great choice for high-traffic websites like e-commerce, search engines, and cloud storage.
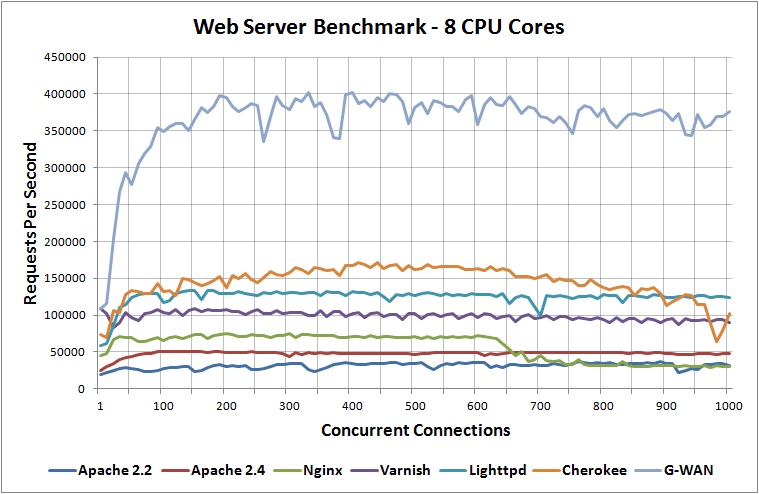
NGINX vs Apache
Among popular web servers, Apache is one of NGINX's main rivals. It has been around since the 90s and has a large community of users. If you are curious to know which is the best web server for your needs, take a look at this brief and informative comparison between NGINX and Apache.
- Operating system compatibility: Compatibility is one of the small details that you should take into account when choosing software. Both NGINX and Apache can run on many operating systems that support Unix. Unfortunately, NGINX performance on Windows is not as good as on other platforms.
- User Support: Users, ranging from newbies to professionals, always need a good community that can help them when they face problems. While NGINX and Apache have email support and a Stack Overflow forum, Apache lacks support from its company, the Apache Foundation.
- Performance: NGINX can simultaneously run 1000 static content connections twice as fast as Apache and uses slightly less memory. However, when compared for their performance in executing dynamic content, both have the same speed. NGINX is a better option for those who have a more static website.
Conclusion
NGINX is a web server that also acts as an email proxy, reverse proxy, and load balancer. The software structure is asynchronous and event-driven; which allows the processing of many requests at the same time. NGINX is also highly scalable, meaning its services grow along with your customers' traffic. NGINX and Apache are, in fact ho, two of the best web servers on the market.